Java下多种执行命令的姿势及问题
Java中执行命令有很多姿势,但是有时候带有|,<,>等符号的命令没办法正常执行。为什么呢?
1 命令执行
要想了解为什么,我们首先需要知道Java中有哪些方式可以执行命令。
1.1 Runtime
package exec;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class RuntimeExec {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InputStream in = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("whoami").getInputStream();
byte[] bcache = new byte[1024];
int readSize = 0; //每次读取的字节长度
ByteArrayOutputStream infoStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
while ((readSize = in.read(bcache)) > 0) {
infoStream.write(bcache, 0, readSize);
}
System.out.println(infoStream.toString());
}
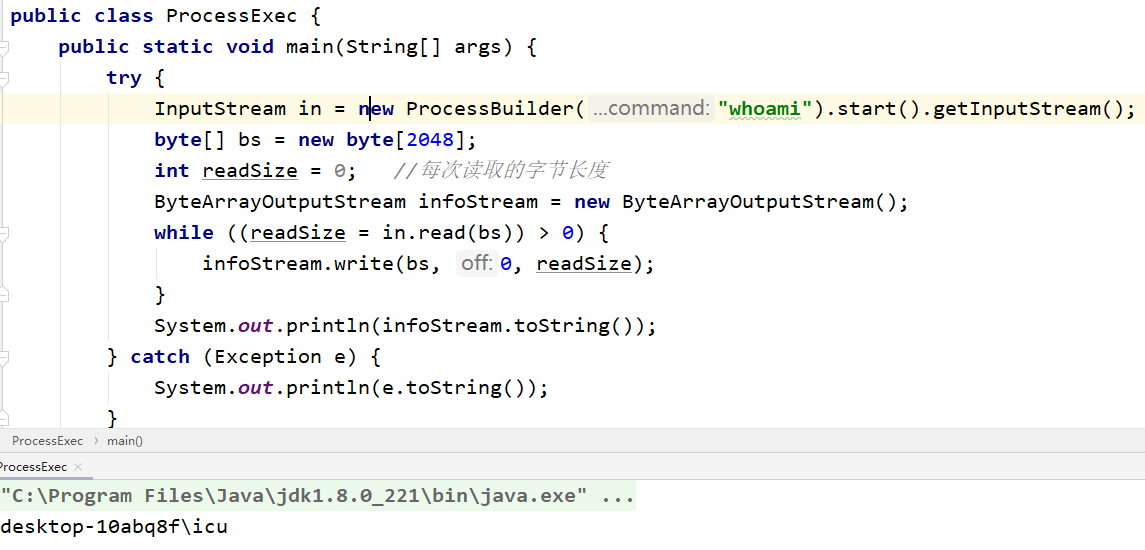
}1.2 ProcessBuilder
package exec;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class ProcessExec {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
InputStream in = new ProcessBuilder("whoami").start().getInputStream();
byte[] bs = new byte[2048];
int readSize = 0; //每次读取的字节长度
ByteArrayOutputStream infoStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
while ((readSize = in.read(bs)) > 0) {
infoStream.write(bs, 0, readSize);
}
System.out.println(infoStream.toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
}1.3 ProcessImpl
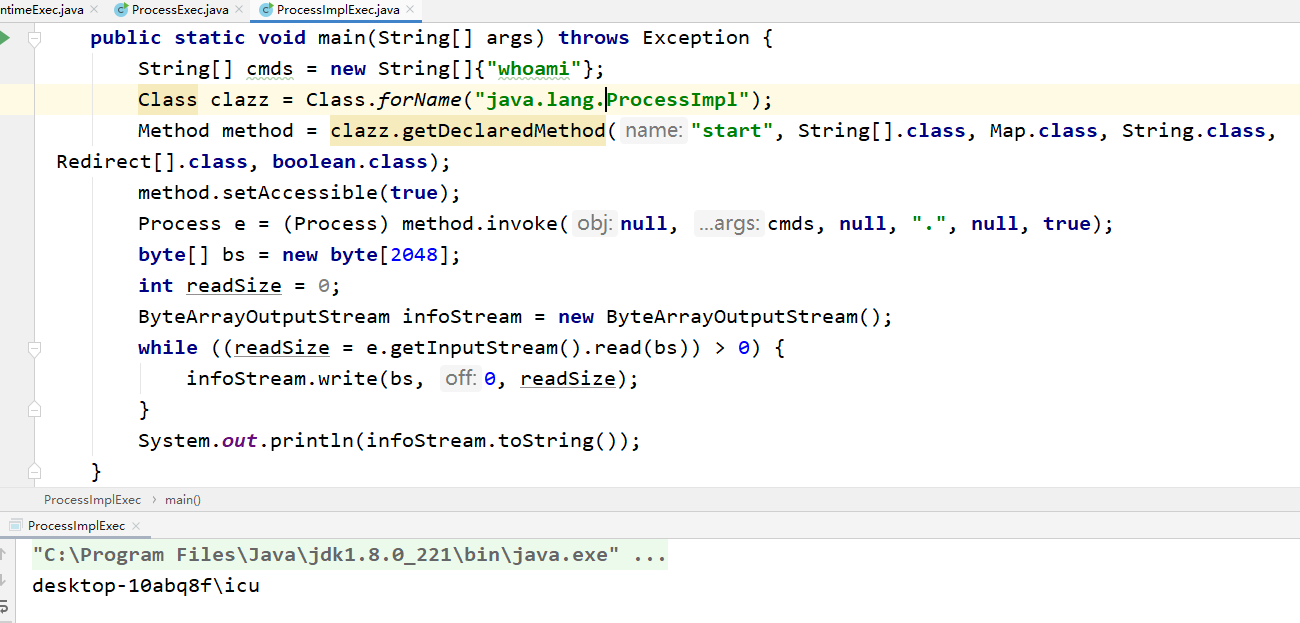
ProcessImpl是更为底层的实现,Runtime和ProcessBuilder执行命令实际上也是调用了ProcessImpl这个类,对于ProcessImpl类我们不能直接调用,但是可以通过反射来间接调用ProcessImpl来达到执行命令的目的。
package exec;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.lang.ProcessBuilder.Redirect;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Map;
public class ProcessImplExec {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String[] cmds = new String[]{"whoami"};
Class clazz = Class.forName("java.lang.ProcessImpl");
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("start", String[].class, Map.class, String.class, Redirect[].class, boolean.class);
method.setAccessible(true);
Process e = (Process) method.invoke(null, cmds, null, ".", null, true);
byte[] bs = new byte[2048];
int readSize = 0;
ByteArrayOutputStream infoStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
while ((readSize = e.getInputStream().read(bs)) > 0) {
infoStream.write(bs, 0, readSize);
}
System.out.println(infoStream.toString());
}
}2 问题
了解了Java中的几种执行命令的函数,我们来看下有什么问题。
2.1 Windows
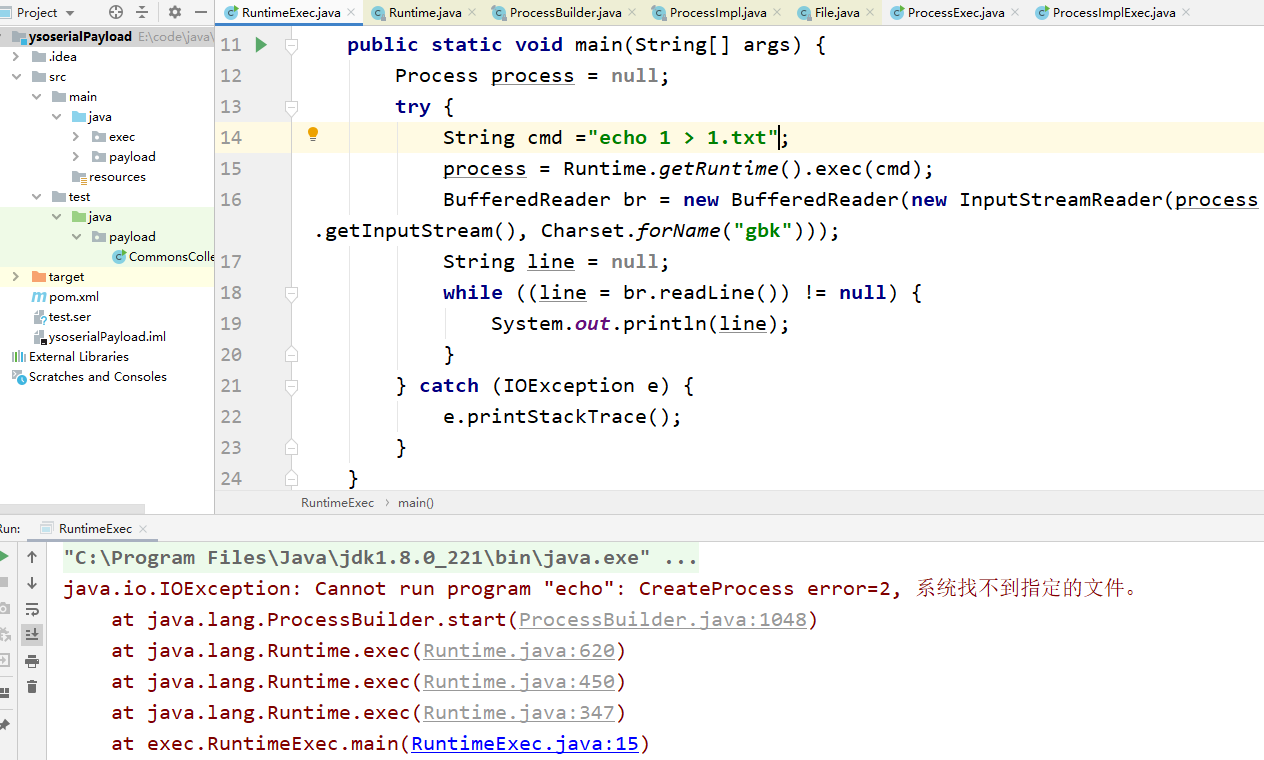
在windows中,命令前缀要加cmd /c
package exec;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Timer;
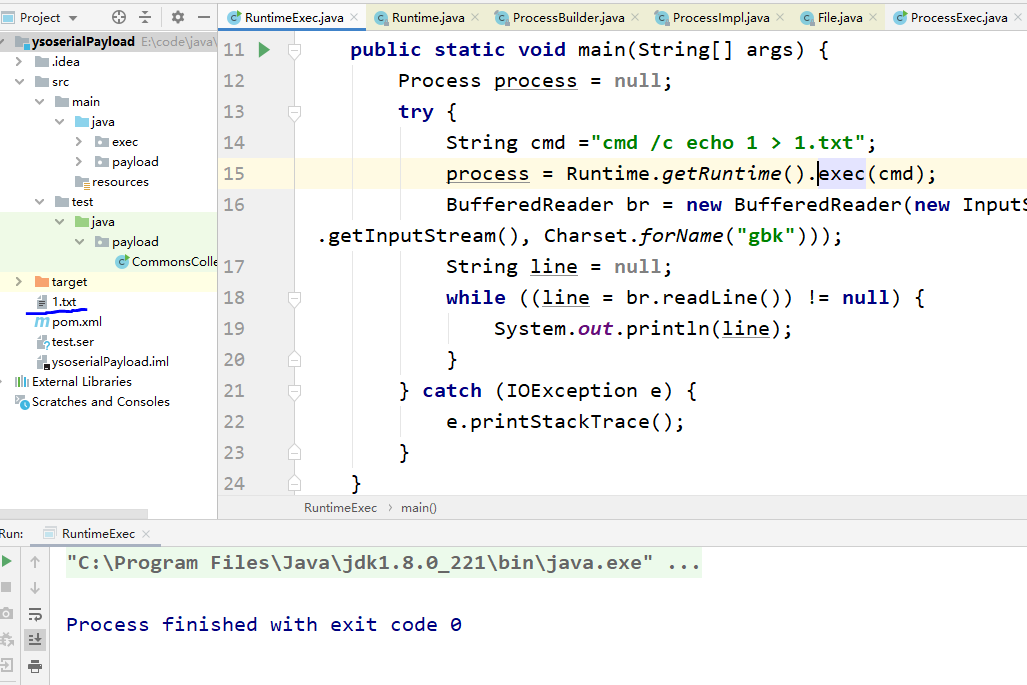
public class RuntimeExec {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Process process = null;
try {
String cmd ="echo 1 > 1.txt";
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream(), Charset.forName("gbk")));
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}加上cmd /c之后
打断点分析下,跟进exec()函数java.lang.Runtime#exec(java.lang.String)
public Process exec(String command) throws IOException {
return exec(command, null, null);
}继续跟进
public Process exec(String command, String[] envp, File dir)
throws IOException {
if (command.length() == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Empty command");
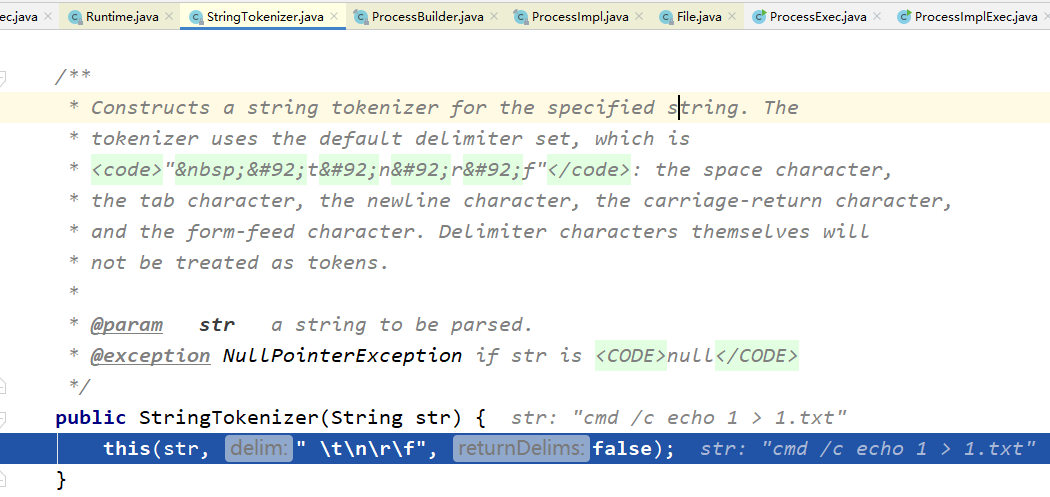
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(command);
String[] cmdarray = new String[st.countTokens()];
for (int i = 0; st.hasMoreTokens(); i++)
cmdarray[i] = st.nextToken();
return exec(cmdarray, envp, dir);
}先判断了command传入的命令是否为空,然后经过StringTokenizer类
继续往下看之后发现,经过StringTokenizer类之后返回了一个以空格分隔的数组
接着往下跟发现走到了
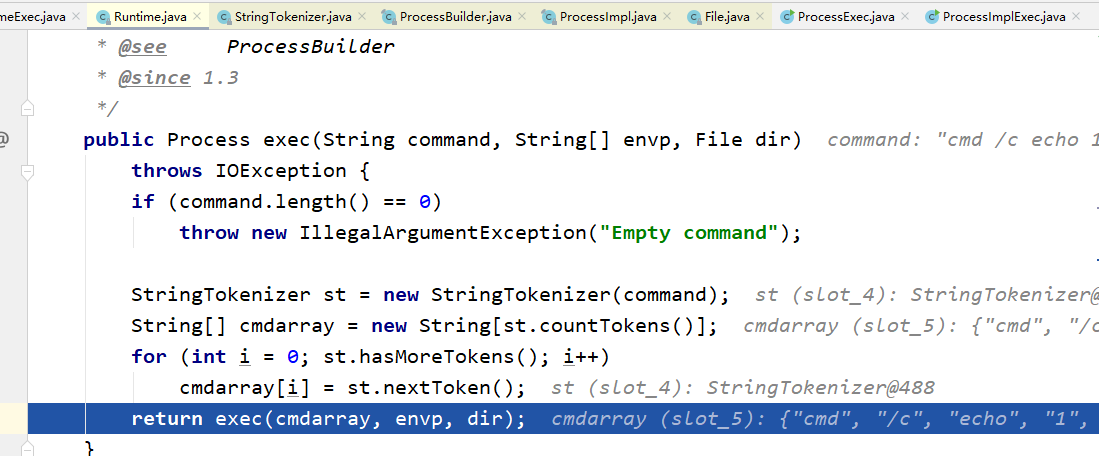
public Process exec(String[] cmdarray, String[] envp, File dir)
throws IOException {
return new ProcessBuilder(cmdarray)
.environment(envp)
.directory(dir)
.start();
}也就是说Runtime的底层实际上还是ProcessBuilder。我们知道ProcessBuilder.start方法是命令执行,那么跟进这个start()。
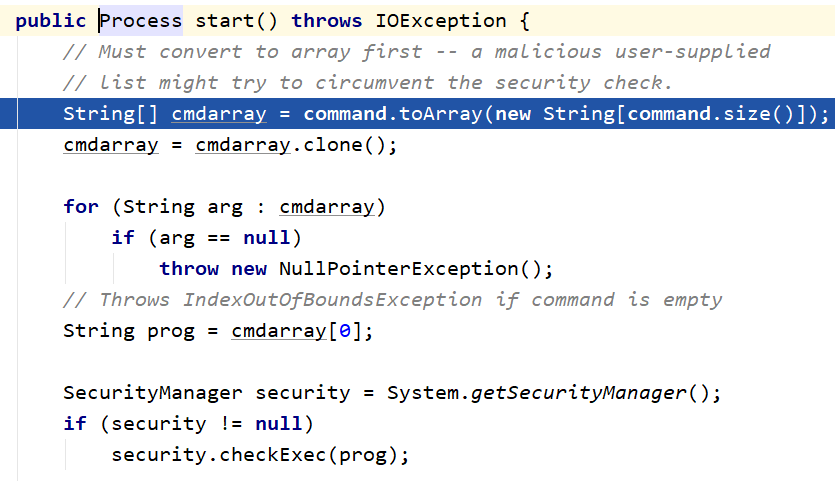
发现String prog = cmdarray[0]拿到的就是我们可执行文件,然后判断security是否为null,如果不为null就会校验checkExec。接下来return了一个java.lang.ProcessImpl.start
也就是说Runtime和ProcessBuilder的底层实际上都是ProcessImpl。而不能执行echo命令的原因是因为java找不到这个东西,也就是没有环境变量。所以加上cmd /c就行了。
2.2 Linux
在谈Linux下的问题时,我们首先要知道一个点
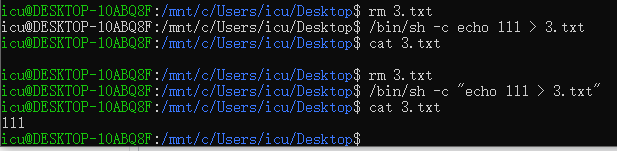
如图所示,/bin/sh -c echo 111 > 3.txt虽然也创建了文件,但是并没有内容,也就是说我们一般通过/bin/sh -c "echo 111 > 3.txt"这种方式来写文件,转化为代码的话就是
String command="/bin/sh -c \"echo 111 > 3.txt\""但是在上文我们知道了一点,StringTokenizer会根据空格将我们的命令划分为数组,那么我们的命令会被划分为{"/bin/sh","-c",""echo","111",">","3.txt""},那么整个命令就变味了,达不到我们想要的效果。
怎么办呢?在ProcessBuilder中有几个构造方法,当传入字符串时会分割为数组
public ProcessBuilder(String... command) {
this.command = new ArrayList<>(command.length);
for (String arg : command)
this.command.add(arg);
}
public ProcessBuilder(List<String> command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.command = command;
}但是传入的是字符串数组时会直接this.command = command,避免了StringTokenizer的空格问题。
package exec;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class RuntimeExec {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Process process = null;
try {
String[] cmd = {"/bin/sh", "-c", "echo 111 > 3.txt"};
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream(), Charset.forName("gbk")));
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}2.3 better?
有没有更好的办法?有的!Linux下可以用bash的base64编码,Windows下用powershell的base64编码。
文笔垃圾,措辞轻浮,内容浅显,操作生疏。不足之处欢迎大师傅们指点和纠正,感激不尽。