警告
本文最后更新于 2019-11-27,文中内容可能已过时。
看明白thinkphp5框架是怎么实现的
thinkphp5.0.24
1
2
3
4
| "require": {
"php": ">=5.4.0",
"topthink/framework": "5.0.*"
},
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| thinkphp/ 根目录
/application 应用目录
/index 应用index模块目录
command.php 命令行命令配置目录
config.php 应用配置文件
databse.php 应用数据库配置文件
route.php 应用路由配置文件
/public 入口目录
/static 静态资源目录
.htacess apache服务器配置
index.php 默认入口文件
robots.txt 爬虫协议文件
router.php php命令行服务器入口文件
/vendor composer安装目录
build.php 默认自动生成配置文件
composer.json composer安装配置文件
console 控制台入口文件
/vendor/topthink/framework 框架核心目录
/extend 框架扩展目录
/lang 框架语言目录
/library 框架核心目录
/mode 框架模式目录
/tests 框架测试目录
/tpl 框架模板目录
/vendor 第三方目录
base.php 全局常量文件
convention.php 全局配置文件
helper.php 辅助函数文件
start.php 框架引导入口
think.php 框架引导文件
|
thinkphp为单程序入口,这是mvc框架的特征,程序的入口在public目录下的index.php
1
2
3
4
| // 定义应用目录
define('APP_PATH', __DIR__ . '/../application/');
// 加载框架引导文件
require __DIR__ . '/../thinkphp/start.php';
|
require引入thinkphp的start.php
1
2
3
4
5
6
| // ThinkPHP 引导文件
// 1. 加载基础文件
require __DIR__ . '/base.php';
// 2. 执行应用
App::run()->send();
|
在base.php(thinkphp/base.php)中定义了一些常量,比如ROOT_PATH、RUNTIME_PATH、LOG_PATH等等,然后引入Loader类来自动加载
1
2
3
| thinkphp/base.php:37
// 载入Loader类
require CORE_PATH . 'Loader.php';
|
然后在下面通过.env文件putenv环境变量,最后
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| // 注册自动加载
\think\Loader::register();
// 注册错误和异常处理机制
\think\Error::register();
// 加载惯例配置文件
\think\Config::set(include THINK_PATH . 'convention' . EXT);
|
在\think\Loader::register()中,使用think\Loader::autoload注册自动加载
1
| spl_autoload_register($autoload ?: 'think\\Loader::autoload', true, true);
|
当PHP引擎遇到试图实例化未知类的操作时,会调用__autoload()方法,并将类名当做字符串参数传递给它。spl_autoload_register会将多个autoload函数以数列的形式依次调用注册。
autoload()的定义,通过名字来引入类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public static function autoload($class)
{
// 检测命名空间别名
if (!empty(self::$namespaceAlias)) {
$namespace = dirname($class);
if (isset(self::$namespaceAlias[$namespace])) {
$original = self::$namespaceAlias[$namespace] . '\\' . basename($class);
if (class_exists($original)) {
return class_alias($original, $class, false);
}
}
}
if ($file = self::findFile($class)) {
// 非 Win 环境不严格区分大小写
if (!IS_WIN || pathinfo($file, PATHINFO_FILENAME) == pathinfo(realpath($file), PATHINFO_FILENAME)) {
__include_file($file);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
|
注册命名空间定义
1
2
3
4
5
| self::addNamespace([
'think' => LIB_PATH . 'think' . DS,
'behavior' => LIB_PATH . 'behavior' . DS,
'traits' => LIB_PATH . 'traits' . DS,
]);
|
加载类库映射文件
1
2
3
| if (is_file(RUNTIME_PATH . 'classmap' . EXT)) {
self::addClassMap(__include_file(RUNTIME_PATH . 'classmap' . EXT));
}
|
注册错误和异常处理机制\think\Error::register()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public static function register()
{
error_reporting(E_ALL);
set_error_handler([__CLASS__, 'appError']);
set_exception_handler([__CLASS__, 'appException']);
register_shutdown_function([__CLASS__, 'appShutdown']);
}
|
将错误、异常、中止时分别交由appError、appException、appShutdown 处理,这三个函数在thinkphp/library/think/Error.php 定义。
接着是加载惯例配置文件
1
| \think\Config::set(include THINK_PATH . 'convention' . EXT);
|
也就是包含thinkphp/convention.php这个配置文件,将配置作为数组变量传入thinkphp/library/think/Config.php:160
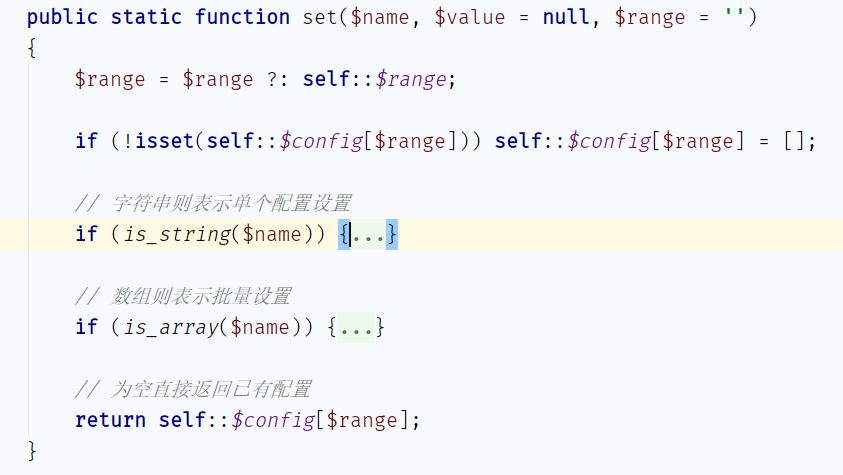 可以通过字符串、数组的形式赋值。配置完之后返回
可以通过字符串、数组的形式赋值。配置完之后返回 thinkphp/start.php:19 启动程序
1
2
| // 2. 执行应用
App::run()->send();
|
thinkphp通过start.php引入的base.php定义文件夹等系统常量,然后引入Loader来加载任意类,通过自动加载使用Error类注册错误处理,以及Config类加载模式配置文件thinkphp/convention.php。做好一系列准备工作之后,执行应用 App::run()->send()
在上文加载完配置等一系列工作之后,进入App::run(),在run()方法中
首先拿到Request的一个实例,然后调用$config = self::initCommon()初始化公共配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| public static function initCommon()
{
if (empty(self::$init)) {
if (defined('APP_NAMESPACE')) {
self::$namespace = APP_NAMESPACE;
}
Loader::addNamespace(self::$namespace, APP_PATH);
// 初始化应用
$config = self::init();
self::$suffix = $config['class_suffix'];
// 应用调试模式
self::$debug = Env::get('app_debug', Config::get('app_debug'));
if (!self::$debug) {
ini_set('display_errors', 'Off');
} elseif (!IS_CLI) {
// 重新申请一块比较大的 buffer
if (ob_get_level() > 0) {
$output = ob_get_clean();
}
ob_start();
if (!empty($output)) {
echo $output;
}
}
if (!empty($config['root_namespace'])) {
Loader::addNamespace($config['root_namespace']);
}
// 加载额外文件
if (!empty($config['extra_file_list'])) {
foreach ($config['extra_file_list'] as $file) {
$file = strpos($file, '.') ? $file : APP_PATH . $file . EXT;
if (is_file($file) && !isset(self::$file[$file])) {
include $file;
self::$file[$file] = true;
}
}
}
// 设置系统时区
date_default_timezone_set($config['default_timezone']);
// 监听 app_init
Hook::listen('app_init');
self::$init = true;
}
return Config::get();
}
|
先Loader::addNamespace(self::$namespace, APP_PATH)添加app所在的命名空间,然后初始化应用$config = self::init(),然后根据self::$debug决定是否将debug信息写入缓冲区,然后根据$config['extra_file_list']的配置来加载额外的配置文件,然后设置时区,hook回调app_init,最后无参数调用Config::get()返回所有全局配置
1
2
3
4
5
| //thinkphp/library/think/Config.php:120
// 无参数时获取所有
if (empty($name) && isset(self::$config[$range])) {
return self::$config[$range];
}
|
初始化应用self::init()的时候
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| private static function init($module = '')
{
// 定位模块目录
$module = $module ? $module . DS : '';
// 加载初始化文件
if (is_file(APP_PATH . $module . 'init' . EXT)) {
include APP_PATH . $module . 'init' . EXT;
} elseif (is_file(RUNTIME_PATH . $module . 'init' . EXT)) {
include RUNTIME_PATH . $module . 'init' . EXT;
} else {
// 加载模块配置
$config = Config::load(CONF_PATH . $module . 'config' . CONF_EXT);
// 读取数据库配置文件
$filename = CONF_PATH . $module . 'database' . CONF_EXT;
Config::load($filename, 'database');
// 读取扩展配置文件
if (is_dir(CONF_PATH . $module . 'extra')) {
$dir = CONF_PATH . $module . 'extra';
$files = scandir($dir);
foreach ($files as $file) {
if ('.' . pathinfo($file, PATHINFO_EXTENSION) === CONF_EXT) {
$filename = $dir . DS . $file;
Config::load($filename, pathinfo($file, PATHINFO_FILENAME));
}
}
}
// 加载应用状态配置
if ($config['app_status']) {
Config::load(CONF_PATH . $module . $config['app_status'] . CONF_EXT);
}
// 加载行为扩展文件
if (is_file(CONF_PATH . $module . 'tags' . EXT)) {
Hook::import(include CONF_PATH . $module . 'tags' . EXT);
}
// 加载公共文件
$path = APP_PATH . $module;
if (is_file($path . 'common' . EXT)) {
include $path . 'common' . EXT;
}
// 加载当前模块语言包
if ($module) {
Lang::load($path . 'lang' . DS . Request::instance()->langset() . EXT);
}
}
return Config::get();
}
|
根据传入的$module判断是模块还是整个应用需要初始化,如果是模块就包含APP_PATH . $module . 'init' . EXT,也就是/application/init.php,如果没传module就包含application/config.php,然后就是加载一些配置文件和语言包。
其实self::initCommon()就是为了拿到全局的配置参数,继续看run方法。
在拿到全局配置$config = self::initCommon();之后,然后根据auto_bind_module和BIND_MODULE两个常量来决定是否需要自动绑定模块,绑定完之后进行了
1
| $request->filter($config['default_filter'])
|
设置当前的过滤规则,然后加载语言,监听app_dispatch应用调度,获取应用调度信息,如果应用调度信息$dispatch为空,则进行路由check $dispatch = self::routeCheck($request, $config),路由check太多了,我拿出来写,然后记录当前调度信息$request->dispatch($dispatch),根据debug写日志,最后检查缓存之后执行了exec函数拿到$data作为response的值,返回response,而exec()才是真正的应用调度函数,会根据$dispatch的值来进入不同的调度模式,也单独拿出来说,至此App.php中就走完了,然后经过thinkphp/start.php的send()发送到客户端。
App::run()是thinkphp程序的主要核心,在其中进行了初始化应用配置–>模块/控制器绑定–>加载语言包–>路由检查–>DEBUG记录–>exec()应用调度–>输出客户端,简单画了一个流程图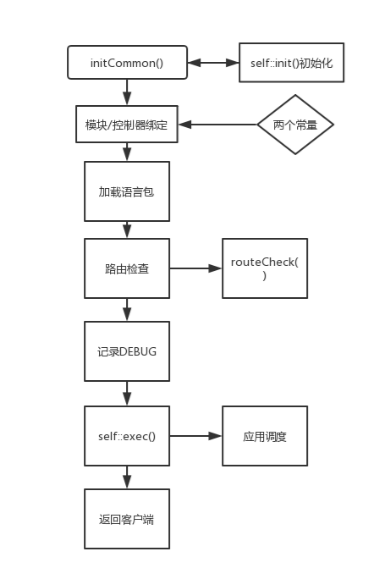
上文中我们说过,在未设置调度信息会进行URL路由检测
1
2
3
| if (empty($dispatch)) {
$dispatch = self::routeCheck($request, $config);
}
|
跟进看下定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| public static function routeCheck($request, array $config)
{
$path = $request->path();
$depr = $config['pathinfo_depr'];
$result = false;
// 路由检测
$check = !is_null(self::$routeCheck) ? self::$routeCheck : $config['url_route_on'];
if ($check) {
// 开启路由
if (is_file(RUNTIME_PATH . 'route.php')) {
// 读取路由缓存
$rules = include RUNTIME_PATH . 'route.php';
is_array($rules) && Route::rules($rules);
} else {
$files = $config['route_config_file'];
foreach ($files as $file) {
if (is_file(CONF_PATH . $file . CONF_EXT)) {
// 导入路由配置
$rules = include CONF_PATH . $file . CONF_EXT;
is_array($rules) && Route::import($rules);
}
}
}
// 路由检测(根据路由定义返回不同的URL调度)
$result = Route::check($request, $path, $depr, $config['url_domain_deploy']);
$must = !is_null(self::$routeMust) ? self::$routeMust : $config['url_route_must'];
if ($must && false === $result) {
// 路由无效
throw new RouteNotFoundException();
}
}
// 路由无效 解析模块/控制器/操作/参数... 支持控制器自动搜索
if (false === $result) {
$result = Route::parseUrl($path, $depr, $config['controller_auto_search']);
}
return $result;
}
|
首先$path是request实例拿到的uri路径,注意是从public目录开始的uri路径,$depr是config.php中定义的pathinfo分隔符,然后进入if语句块,如果有路由缓存会读路由缓存,没有的话会读/application/route.php导入路由,经过Route::check()后,会拿$config['url_route_must']来判断是否是强路由
1
2
| // 是否强制使用路由
'url_route_must' => false,
|
如果是强路由会抛出throw new RouteNotFoundException() 异常,如果没有开启强路由会进入Route::parseUrl($path, $depr, $config['controller_auto_search'])自动解析模块/控制器/操作/参数
先跟进到Route::check()康康
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| public static function check($request, $url, $depr = '/', $checkDomain = false)
{
//检查解析缓存
if (!App::$debug && Config::get('route_check_cache')) {
$key = self::getCheckCacheKey($request);
if (Cache::has($key)) {
list($rule, $route, $pathinfo, $option, $matches) = Cache::get($key);
return self::parseRule($rule, $route, $pathinfo, $option, $matches, true);
}
}
// 分隔符替换 确保路由定义使用统一的分隔符
$url = str_replace($depr, '|', $url);
if (isset(self::$rules['alias'][$url]) || isset(self::$rules['alias'][strstr($url, '|', true)])) {
// 检测路由别名
$result = self::checkRouteAlias($request, $url, $depr);
if (false !== $result) {
return $result;
}
}
$method = strtolower($request->method());
// 获取当前请求类型的路由规则
$rules = isset(self::$rules[$method]) ? self::$rules[$method] : [];
// 检测域名部署
if ($checkDomain) {
self::checkDomain($request, $rules, $method);
}
// 检测URL绑定
$return = self::checkUrlBind($url, $rules, $depr);
if (false !== $return) {
return $return;
}
if ('|' != $url) {
$url = rtrim($url, '|');
}
$item = str_replace('|', '/', $url);
if (isset($rules[$item])) {
// 静态路由规则检测
$rule = $rules[$item];
if (true === $rule) {
$rule = self::getRouteExpress($item);
}
if (!empty($rule['route']) && self::checkOption($rule['option'], $request)) {
self::setOption($rule['option']);
return self::parseRule($item, $rule['route'], $url, $rule['option']);
}
}
// 路由规则检测
if (!empty($rules)) {
return self::checkRoute($request, $rules, $url, $depr);
}
return false;
}
|
首先检查路由缓存,默认config.php中是不开启路由缓存的,然后检测路由别名
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| private static $rules = [
'get' => [],
'post' => [],
'put' => [],
'delete' => [],
'patch' => [],
'head' => [],
'options' => [],
'*' => [],
'alias' => [],
'domain' => [],
'pattern' => [],
'name' => [],
];
|
如果路由存在别名会进入checkRouteAlias(),在这个函数内会直接进入到路由对应的模块/控制器/操作。如果不存在别名会继续检查,然后是获取当前请求类型的路由规则->检测域名部署checkDomain()->检测URL绑定checkUrlBind(),然后会判断是否是静态路由,如果是会返回parseRule(),不然返回self::checkRoute($request, $rules, $url, $depr)。
在这里我要提一手thinkphp的多种路由定义
| 定义方式 | 定义格式 |
|---|
| 方式1:路由到模块/控制器 | ‘[模块/控制器/操作]?额外参数1=值1&额外参数2=值2…’ |
| 方式2:路由到重定向地址 | ‘外部地址’(默认301重定向) 或者 [‘外部地址’,‘重定向代码’] |
| 方式3:路由到控制器的方法 | ‘@[模块/控制器/]操作’ |
| 方式4:路由到类的方法 | ‘\完整的命名空间类::静态方法’ 或者 ‘\完整的命名空间类@动态方法’ |
| 方式5:路由到闭包函数 | 闭包函数定义(支持参数传入) |
因为多种路由模式的支持,所以程序的流程也不尽相同,我这里只分析第一种模块/控制器/操作的形式。再看App::routeCheck(),如果不是route.php定义的路由并且没有开启强路由会开始自动搜索控制器
1
2
3
4
| // 路由无效 解析模块/控制器/操作/参数... 支持控制器自动搜索
if (false === $result) {
$result = Route::parseUrl($path, $depr, $config['controller_auto_search']);
}
|
最终程序会进入parseUrl()来解析url,在parseUrl()中会解析url参数parseUrlParams(),这两个函数就不分析了,就是单纯的分割参数存储数组,最后会return一个['type' => 'module', 'module' => $route]
说的不是很明白,我这边直接访问
1
| http://php.local/public/index.php?s=index/index/index/id/1
|
那么可以看到parseUrl()返回的就是一个数组,数组中存放着模块控制器/操作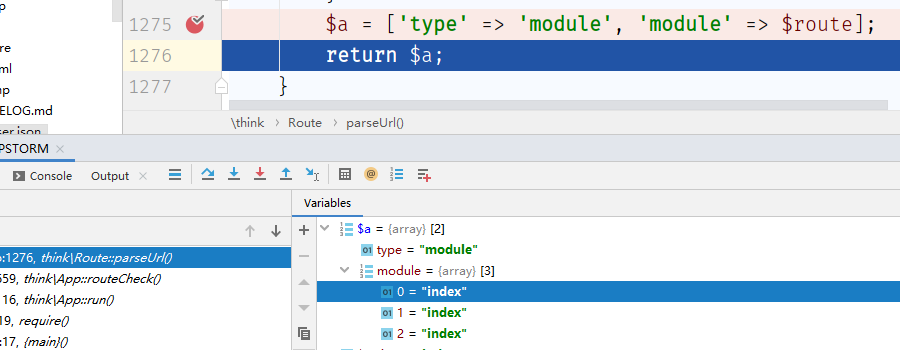 那么
那么routeCheck()返回的$result会作为thinkphp/library/think/App.php:116的$dispatch的值,进入到exec()的应用调度中。
又臭又长的文字不如一张图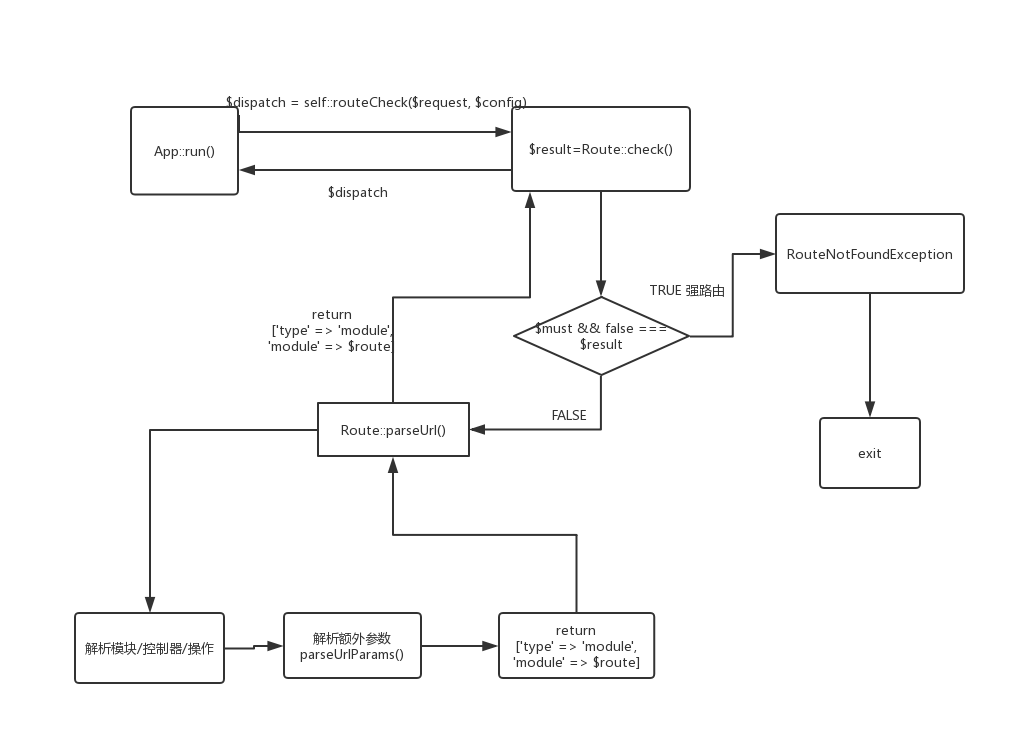
我们上文提到了routeCheck()返回的$dispatch会进入到exec()函数中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| protected static function exec($dispatch, $config)
{
switch ($dispatch['type']) {
case 'redirect': // 重定向跳转
$data = Response::create($dispatch['url'], 'redirect')
->code($dispatch['status']);
break;
case 'module': // 模块/控制器/操作
$data = self::module(
$dispatch['module'],
$config,
isset($dispatch['convert']) ? $dispatch['convert'] : null
);
break;
case 'controller': // 执行控制器操作
$vars = array_merge(Request::instance()->param(), $dispatch['var']);
$data = Loader::action(
$dispatch['controller'],
$vars,
$config['url_controller_layer'],
$config['controller_suffix']
);
break;
case 'method': // 回调方法
$vars = array_merge(Request::instance()->param(), $dispatch['var']);
$data = self::invokeMethod($dispatch['method'], $vars);
break;
case 'function': // 闭包
$data = self::invokeFunction($dispatch['function']);
break;
case 'response': // Response 实例
$data = $dispatch['response'];
break;
default:
throw new \InvalidArgumentException('dispatch type not support');
}
return $data;
}
|
在这个方法中会根据不同的$dispatch['type']调度类型来进行区别处理,其中除了redirect和response之外的case语句块都会调用App内的静态方法通过反射实现调用模块/控制器/操作
1
2
3
4
| module调度类型的self::module() -> self::invokeMethod()
controller调度类型的Loader::action() -> 进入App::invokeMethod()
method调度类型的self::invokeMethod()
function调度类型的self::invokeFunction()
|
看定义invokeMethod()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public static function invokeMethod($method, $vars = [])
{
if (is_array($method)) {
$class = is_object($method[0]) ? $method[0] : self::invokeClass($method[0]);
$reflect = new \ReflectionMethod($class, $method[1]);
} else {
// 静态方法
$reflect = new \ReflectionMethod($method);
}
$args = self::bindParams($reflect, $vars);
self::$debug && Log::record('[ RUN ] ' . $reflect->class . '->' . $reflect->name . '[ ' . $reflect->getFileName() . ' ]', 'info');
return $reflect->invokeArgs(isset($class) ? $class : null, $args);
}
|
在invokeMethod()中,创建反射方法$reflect = new \ReflectionMethod($class, $method[1]);,获取反射函数$args = self::bindParams($reflect, $vars);,接着记录日志后调用$reflect->invokeArgs(isset($class) ? $class : null, $args);反射调用模块/控制器/操作中的操作。
为了方便解释我在index控制器创建了hello方法
1
2
3
4
| public function hello($name)
{
return 'hello' . $name;
}
|
然后访问
1
| http://php.local/public/index.php?s=index/index/hello/name/aaa
|
此时模块调度进入module的case语句
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| case 'module': // 模块/控制器/操作
$data = self::module(
$dispatch['module'],
$config,
isset($dispatch['convert']) ? $dispatch['convert'] : null
);
break;
|
在module方法中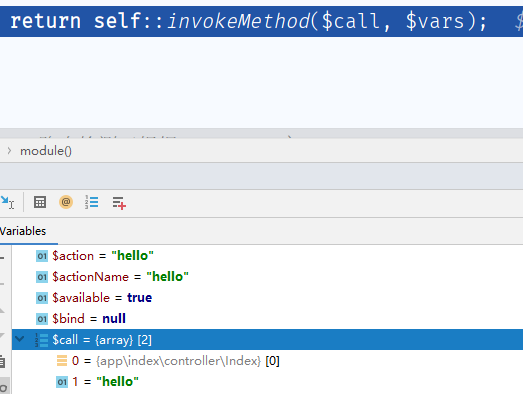 最后return的是就是我们的
最后return的是就是我们的hello方法,但是此时的参数是空的,而我们传入有name=aaa参数,那么这个参数在哪赋值的呢?跟进反射看看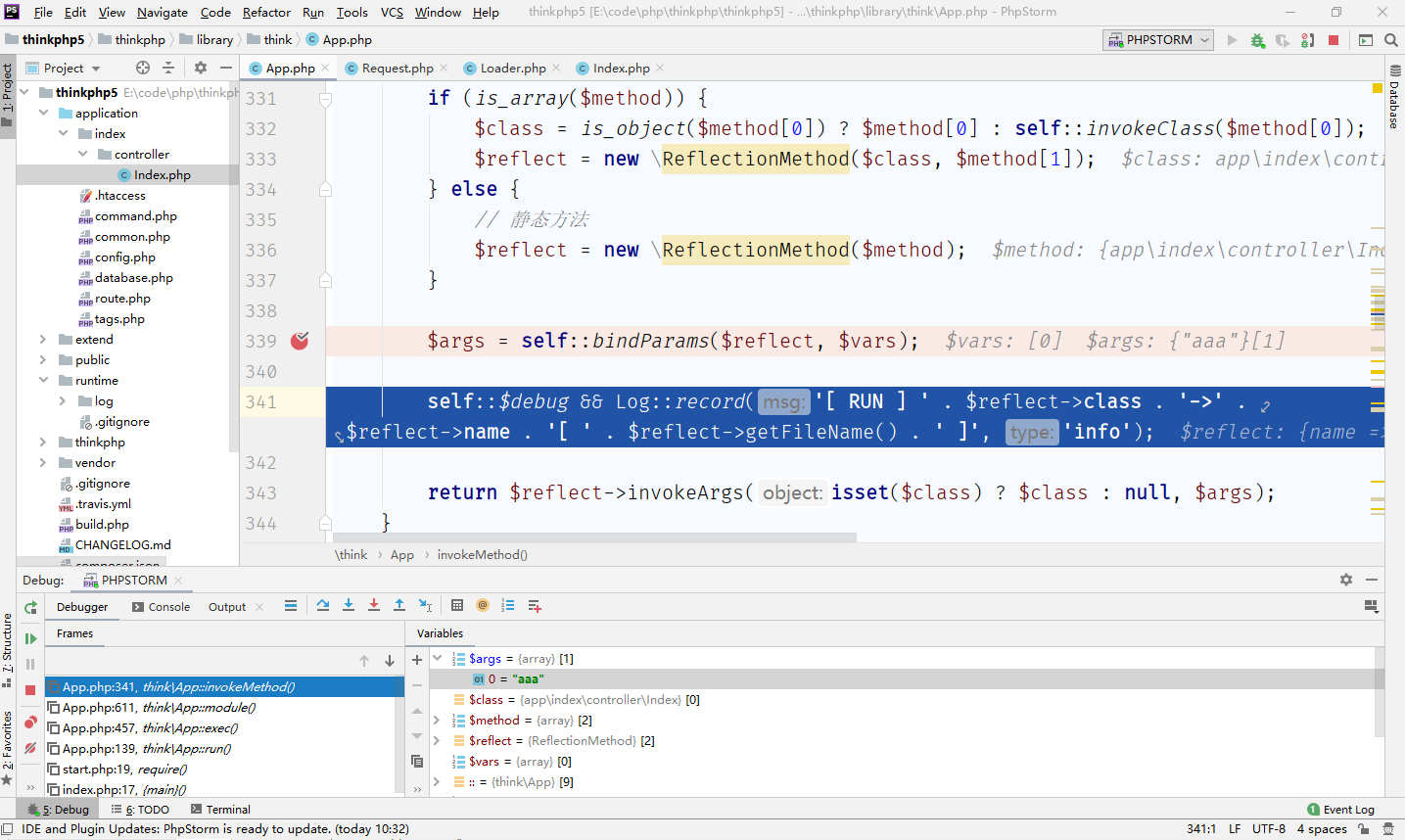 在339行,
在339行,$args = self::bindParams($reflect, $vars)作为invokeArgs()的反射参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| private static function bindParams($reflect, $vars = [])
{
// 自动获取请求变量
if (empty($vars)) {
$vars = Config::get('url_param_type') ?
Request::instance()->route() :
Request::instance()->param();
}
$args = [];
if ($reflect->getNumberOfParameters() > 0) {
// 判断数组类型 数字数组时按顺序绑定参数
reset($vars);
$type = key($vars) === 0 ? 1 : 0;
foreach ($reflect->getParameters() as $param) {
$args[] = self::getParamValue($param, $vars, $type);
}
}
return $args;
}
|
args会从Request::instance()->route()或者Request::instance()->param();获取,也就是request中获取。这样就实现了从url中达到动态调用模块/控制器/操作的目的。
应用调度就是这样完成他的使命,一个switch语句判断$dispatch['type'],然后进入不同的处理,如果实现业务逻辑则会通过反射类调用相应的模块/控制器/操作函数,拿到操作返回的数据之后整个exec()函数就结束了。最终继续执行App::run()方法返回response对象,进入send()方法返回给客户端,整个流程结束。
请求类处于thinkphp/library/think/Request.php,众所周知的是thinkphp有助手函数input()来获取请求参数,本节说一下thinkphp中具体怎么实现的。
我们先来给一个控制器来做演示
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public function hello($name)
{
if(input('?name')){
var_dump(input('?name'));
return input('name');
}else{
return '没有设置name参数!';
}
}
|
助手函数input()可以这么写:
1
2
3
4
5
| input('param.name');
input('param.');
或者
input('name');
input('');
|
判断有没有传递某个参数可以用
1
2
| input('?get.id');
input('?post.name');
|
我们打断点跟进下,进入到thinkphp/helper.php:121
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| function input($key = '', $default = null, $filter = '')
{
if (0 === strpos($key, '?')) {
$key = substr($key, 1);
$has = true;
}
if ($pos = strpos($key, '.')) {
// 指定参数来源
list($method, $key) = explode('.', $key, 2);
if (!in_array($method, ['get', 'post', 'put', 'patch', 'delete', 'route', 'param', 'request', 'session', 'cookie', 'server', 'env', 'path', 'file'])) {
$key = $method . '.' . $key;
$method = 'param';
}
} else {
// 默认为自动判断
$method = 'param';
}
if (isset($has)) {
return request()->has($key, $method, $default);
} else {
return request()->$method($key, $default, $filter);
}
}
|
第一个if是为了来判断是否传递某个参数
1
2
| input('?get.id');
input('?post.name');
|
这种写法,会进入request()->has($key, $method, $default),request()方法会返回一个request类的实例
1
2
3
4
| function request()
{
return Request::instance();
}
|
has()方法会返回一个布尔值来决定是否传递了这个参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public function has($name, $type = 'param', $checkEmpty = false)
{
if (empty($this->$type)) {
$param = $this->$type();
} else {
$param = $this->$type;
}
// 按.拆分成多维数组进行判断
foreach (explode('.', $name) as $val) {
if (isset($param[$val])) {
$param = $param[$val];
} else {
return false;
}
}
return ($checkEmpty && '' === $param) ? false : true;
}
|
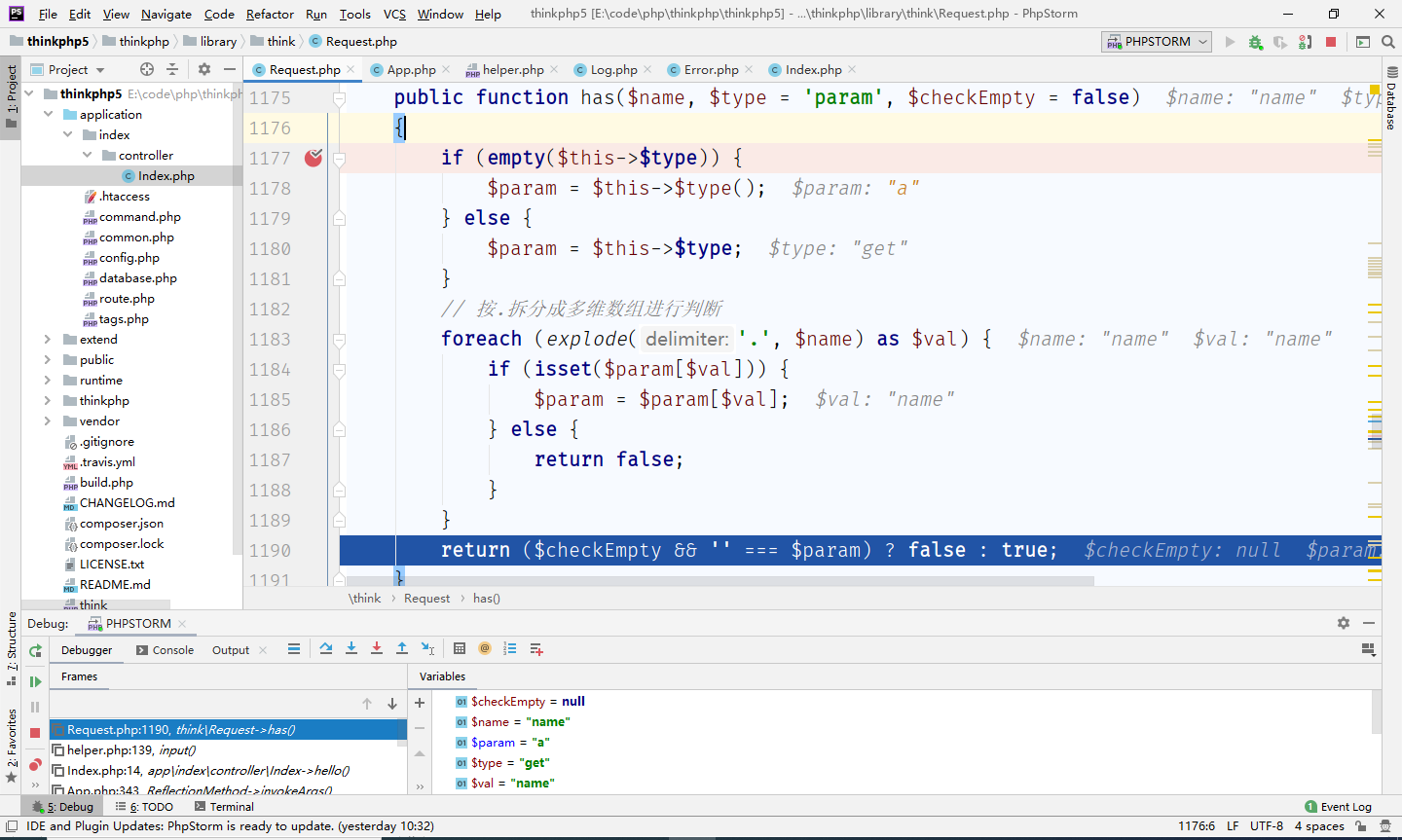 此时访问
此时访问
1
| http://php.local/public/index.php?s=index/index/hello/name/aaa
|
页面则会返回 到此只是判断某个参数是否存在,是
到此只是判断某个参数是否存在,是input('?name')这种语法,我们继续跟进input('name')这种语法,他会进入
1
| return request()->$method($key, $default, $filter);
|
当没有包含?或.时,
1
2
| input('?name')
input('?get.name')
|
会进入request()->$method($key, $default, $filter),此时会进入的就是request类中的param()方法,跟进
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public function param($name = '', $default = null, $filter = '')
{
if (empty($this->mergeParam)) {
$method = $this->method(true);
// 自动获取请求变量
switch ($method) {
case 'POST':
$vars = $this->post(false);
break;
case 'PUT':
case 'DELETE':
case 'PATCH':
$vars = $this->put(false);
break;
default:
$vars = [];
}
// 当前请求参数和URL地址中的参数合并
$this->param = array_merge($this->param, $this->get(false), $vars, $this->route(false));
$this->mergeParam = true;
}
if (true === $name) {
// 获取包含文件上传信息的数组
$file = $this->file();
$data = is_array($file) ? array_merge($this->param, $file) : $this->param;
return $this->input($data, '', $default, $filter);
}
return $this->input($this->param, $name, $default, $filter);
}
|
param()方法会将原生$_GET、$_POST等全局数组的参数合并到$this->param,然后进入$this->input()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| public function input($data = [], $name = '', $default = null, $filter = '')
{
if (false === $name) {
// 获取原始数据
return $data;
}
$name = (string)$name;
if ('' != $name) {
// 解析name
if (strpos($name, '/')) {
list($name, $type) = explode('/', $name);
} else {
$type = 's';
}
// 按.拆分成多维数组进行判断
foreach (explode('.', $name) as $val) {
if (isset($data[$val])) {
$data = $data[$val];
} else {
// 无输入数据,返回默认值
return $default;
}
}
if (is_object($data)) {
return $data;
}
}
// 解析过滤器
$filter = $this->getFilter($filter, $default);
if (is_array($data)) {
array_walk_recursive($data, [$this, 'filterValue'], $filter);
reset($data);
} else {
$this->filterValue($data, $name, $filter);
}
if (isset($type) && $data !== $default) {
// 强制类型转换
$this->typeCast($data, $type);
}
return $data;
}
|
可以看出来input()是用来接收参数,并且经过了一层filterValue()过滤和$this->typeCast($data, $type)强制类型转换
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| private function filterValue(&$value, $key, $filters)
{
$default = array_pop($filters);
foreach ($filters as $filter) {
if (is_callable($filter)) {
// 调用函数或者方法过滤
$value = call_user_func($filter, $value);
} elseif (is_scalar($value)) {
if (false !== strpos($filter, '/')) {
// 正则过滤
if (!preg_match($filter, $value)) {
// 匹配不成功返回默认值
$value = $default;
break;
}
} elseif (!empty($filter)) {
// filter函数不存在时, 则使用filter_var进行过滤
// filter为非整形值时, 调用filter_id取得过滤id
$value = filter_var($value, is_int($filter) ? $filter : filter_id($filter));
if (false === $value) {
$value = $default;
break;
}
}
}
}
return $this->filterExp($value);
}
|
filterValue()会使用$fileter通过call_user_func来回调过滤,thinkphp5.x的rce就是覆盖此处的$filter为system()来执行命令,最后会$filterExp过滤关键字符
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public function filterExp(&$value)
{
// 过滤查询特殊字符
if (is_string($value) && preg_match('/^(EXP|NEQ|GT|EGT|LT|ELT|OR|XOR|LIKE|NOTLIKE|NOT LIKE|NOT BETWEEN|NOTBETWEEN|BETWEEN|NOT EXISTS|NOTEXISTS|EXISTS|NOT NULL|NOTNULL|NULL|BETWEEN TIME|NOT BETWEEN TIME|NOTBETWEEN TIME|NOTIN|NOT IN|IN)$/i', $value)) {
$value .= ' ';
}
// TODO 其他安全过滤
}
|
thinkphp3.2.3的exp和bind注入就出自此处。再来看上文的强制类型转换$this->typeCast($data, $type)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| private function typeCast(&$data, $type)
{
switch (strtolower($type)) {
// 数组
case 'a':
$data = (array)$data;
break;
// 数字
case 'd':
$data = (int)$data;
break;
// 浮点
case 'f':
$data = (float)$data;
break;
// 布尔
case 'b':
$data = (boolean)$data;
break;
// 字符串
case 's':
default:
if (is_scalar($data)) {
$data = (string)$data;
} else {
throw new \InvalidArgumentException('variable type error:' . gettype($data));
}
}
}
|
此时可知 input()助手函数 ->request类param() -> request类input()获取参数
我们此时再来看下request类,这个类中有很多函数,比如get()、post()、put()、env()、delete()等,其实他们最终都会流向input()函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public function get($name = '', $default = null, $filter = '')
{
if (empty($this->get)) {
$this->get = $_GET;
}
if (is_array($name)) {
$this->param = [];
$this->mergeParam = false;
return $this->get = array_merge($this->get, $name);
}
return $this->input($this->get, $name, $default, $filter);
}
|
比如get()会合并$_GET数组中的参数然后传入input()。
Request类是一个获取请求类,thinkphp将多种请求的全局数组封装了一下,变为自己的函数,并且进行了过滤和强制类型转换,以此保证参数的安全性。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <?php
namespace app\index\controller;
use think\Controller;
class Index extends Controller
{
public function index($name)
{
$this->assign('name',$name);
return $this->fetch();
}
}
|
写一个index方法来赋值变量并渲染模板,需要注意继承父类Controller,不然没法使用assign和fetch。创建模板文件application/index/view/index/index.html,内容为
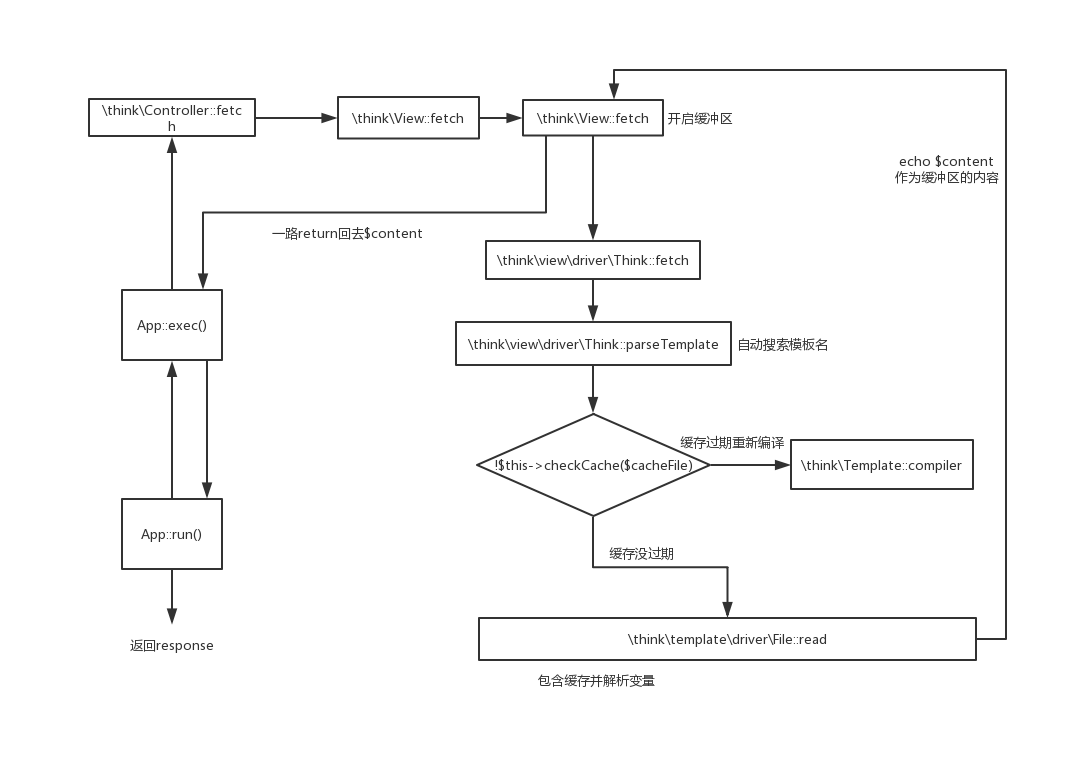
然后我们来康康thinkphp是怎么实现的模板功能,打断点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| //thinkphp/library/think/Controller.php
protected function assign($name, $value = '')
{
$this->view->assign($name, $value);
return $this;
}
|
跟进$this->view->assign()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public function assign($name, $value = '')
{
if (is_array($name)) {
$this->data = array_merge($this->data, $name);
} else {
$this->data[$name] = $value;
}
return $this;
}
|
这个方法中把赋给模板的参数合并到$this->data,然后返回进入$this->fetch(),
1
2
3
4
5
| //thinkphp/library/think/Controller.php:118
protected function fetch($template = '', $vars = [], $replace = [], $config = [])
{
return $this->view->fetch($template, $vars, $replace, $config);
}
|
继续跟进
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public function fetch($template = '', $vars = [], $replace = [], $config = [], $renderContent = false)
{
// 模板变量
$vars = array_merge(self::$var, $this->data, $vars);
// 页面缓存
ob_start();
ob_implicit_flush(0);
// 渲染输出
try {
$method = $renderContent ? 'display' : 'fetch';
// 允许用户自定义模板的字符串替换
$replace = array_merge($this->replace, $replace, (array) $this->engine->config('tpl_replace_string'));
$this->engine->config('tpl_replace_string', $replace);
$this->engine->$method($template, $vars, $config);
} catch (\Exception $e) {
ob_end_clean();
throw $e;
}
// 获取并清空缓存
$content = ob_get_clean();
// 内容过滤标签
Hook::listen('view_filter', $content);
return $content;
}
|
先开启缓冲区,然后定义变量用来存放用户自定义的需要替换的字符串,进入config()函数中做渲染引擎初始化配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public function config($name, $value = null)
{
if (is_array($name)) {
$this->template->config($name);
$this->config = array_merge($this->config, $name);
} elseif (is_null($value)) {
return $this->template->config($name);
} else {
$this->template->$name = $value;
$this->config[$name] = $value;
}
}
|
然后进入$this->engine->$method($template, $vars, $config);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public function fetch($template, $data = [], $config = [])
{
if ('' == pathinfo($template, PATHINFO_EXTENSION)) {
// 获取模板文件名
$template = $this->parseTemplate($template);
}
// 模板不存在 抛出异常
if (!is_file($template)) {
throw new TemplateNotFoundException('template not exists:' . $template, $template);
}
// 记录视图信息
App::$debug && Log::record('[ VIEW ] ' . $template . ' [ ' . var_export(array_keys($data), true) . ' ]', 'info');
$this->template->fetch($template, $data, $config);
}
|
当没有传模板名时会使用$this->parseTemplate($template)来自动搜索模板文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| private function parseTemplate($template)
{
...
if ($this->config['view_base']) {
// 基础视图目录
$module = isset($module) ? $module : $request->module();
$path = $this->config['view_base'] . ($module ? $module . DS : '');
} else {
$path = isset($module) ? APP_PATH . $module . DS . 'view' . DS : $this->config['view_path'];
}
$depr = $this->config['view_depr'];
if (0 !== strpos($template, '/')) {
$template = str_replace(['/', ':'], $depr, $template);
$controller = Loader::parseName($request->controller());
if ($controller) {
if ('' == $template) {
// 如果模板文件名为空 按照默认规则定位
$template = str_replace('.', DS, $controller) . $depr . (1 == $this->config['auto_rule'] ? Loader::parseName($request->action(true)) : $request->action());
}
...
}
}
...
return $path . ltrim($template, '/') . '.' . ltrim($this->config['view_suffix'], '.');
}
|
最后返回的就是E:\code\php\thinkphp\thinkphp5\public/../application/index\view\index\index.html,这是默认的模板位置,然后debug之后又进入$this->template->fetch($template, $data, $config)
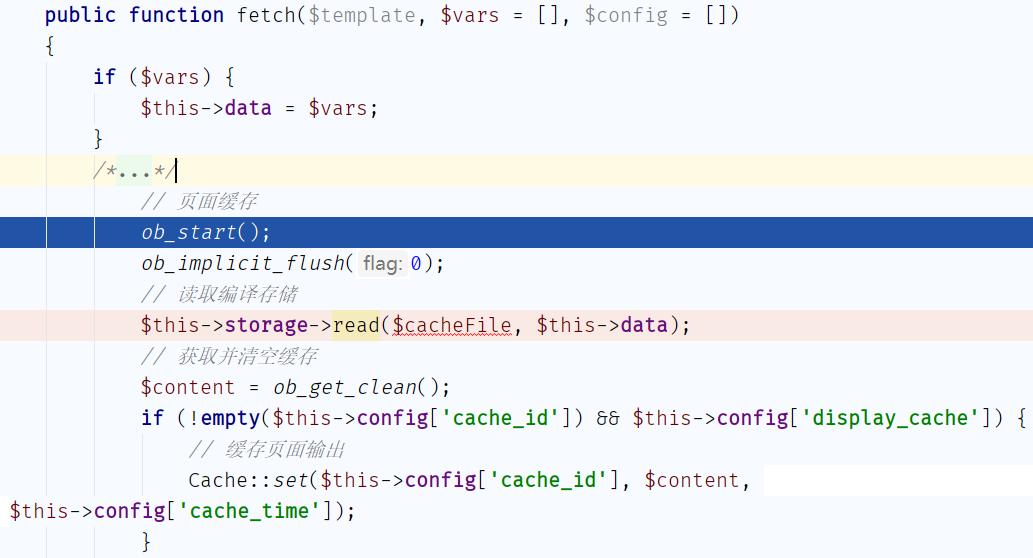 为了方便看流程,我注释掉了部分代码,可以看到首先是
为了方便看流程,我注释掉了部分代码,可以看到首先是$this->data = $vars;将参数合并到data中,然后开启缓冲区,进入$this->storage->read($cacheFile, $this->data),然后输出$content,最后$content就是我们模板已经被解析过的内容。那么我们进入$this->storage->read()看下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public function read($cacheFile, $vars = [])
{
$this->cacheFile = $cacheFile;
if (!empty($vars) && is_array($vars)) {
// 模板阵列变量分解成为独立变量
extract($vars, EXTR_OVERWRITE);
}
//载入模版缓存文件
include $this->cacheFile;
}
|
会将我们的参数进行变量覆盖,然后包含缓存文件,也就是我们的模板文件,在包含的时候缓冲区就写入了渲染完成的模板的内容,而后$content获取到的就是渲染的内容,这就是全部流程。
thinkphp那么多的代码不是我一篇文章就能说完的,阅读thinkphp的源码你需要对thinkphp的开发流程及php的函数特性有着足够深入的了解,在本文中只是简单介绍了thinkphp的实现过程,有很多东西没有时间和精力去写笔记,比如模板解析、Model层、数据库交互、模板缓存等是怎么实现的,东西是写给自己看的,如果有前辈或者后人看到了这篇文章,请多谅解。
文笔垃圾,措辞轻浮,内容浅显,操作生疏。不足之处欢迎大师傅们指点和纠正,感激不尽。












